Understanding the Composition of Matter: A Deep Dive into the Makeup of Things
Related Articles: Understanding the Composition of Matter: A Deep Dive into the Makeup of Things
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Composition of Matter: A Deep Dive into the Makeup of Things. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Composition of Matter: A Deep Dive into the Makeup of Things

The world around us, from the smallest atom to the vastest galaxy, is composed of matter. This matter, in turn, is made up of fundamental building blocks – elements. Each element is unique, possessing distinct properties that define its behavior and interactions. Understanding the makeup of things, the arrangement and combination of these elements, is crucial for comprehending the nature of the universe and the countless materials that populate it.
This article delves into the fascinating world of matter’s composition, exploring the fundamental concepts that underpin our understanding of the physical world. We will journey from the basic building blocks of atoms to the complex structures of molecules and delve into the ways in which these components interact to form the diverse materials that shape our lives.
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
At the heart of every material lies the atom, the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Each atom consists of a central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus, in turn, is composed of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons.
The number of protons within an atom’s nucleus, known as the atomic number, defines the element. For instance, all carbon atoms have six protons, while all oxygen atoms have eight. This fundamental property dictates an element’s chemical behavior, determining how it interacts with other elements to form new substances.
Elements: The Unique Components of Matter
The periodic table, a familiar chart to most science enthusiasts, organizes all known elements in order of increasing atomic number. This arrangement reveals recurring patterns in their properties, enabling scientists to predict and understand the behavior of different elements.
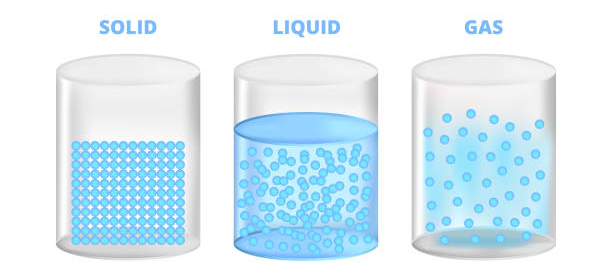
The diversity of elements is vast, ranging from the lightest element, hydrogen, to the heaviest naturally occurring element, uranium. Each element possesses unique characteristics, including its physical state at room temperature (solid, liquid, or gas), its melting and boiling points, its density, and its reactivity.
Molecules: The Building Blocks of Compounds
Atoms rarely exist in isolation. They bond together to form molecules, the smallest unit of a compound that retains the compound’s chemical properties. The process of bond formation involves the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in a stable arrangement.
The nature of the chemical bond dictates the properties of the resulting molecule. For example, the strong covalent bond between carbon atoms in diamonds results in an incredibly hard and durable material, while the weaker hydrogen bonds between water molecules contribute to water’s unique properties, such as its high boiling point and ability to dissolve many substances.
Compounds: Combining Elements into New Substances
When two or more elements combine in a fixed ratio, they form a compound. Compounds have distinct properties that differ from the properties of their constituent elements. For example, sodium (a highly reactive metal) and chlorine (a poisonous gas) combine to form sodium chloride (table salt), a compound with entirely different properties.
The diversity of compounds is vast, encompassing everything from simple molecules like water (H2O) to complex polymers like plastics and proteins. Each compound possesses a unique chemical formula, reflecting the specific arrangement and ratio of its constituent elements.
The Importance of Understanding the Makeup of Things
The knowledge of the makeup of things is fundamental to various fields, including chemistry, materials science, medicine, and engineering. It allows us to:
- Develop new materials: By understanding the properties of elements and their interactions, scientists can design and synthesize novel materials with specific desired properties. For instance, the development of high-strength alloys for aerospace applications or the creation of biodegradable plastics for environmental sustainability.
- Understand biological processes: The composition of living organisms is incredibly complex, with molecules like DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates playing vital roles in life processes. Understanding the makeup of these molecules is crucial for comprehending how organisms function, evolve, and respond to their environment.
- Develop new technologies: From the creation of new pharmaceuticals to the design of efficient solar cells, understanding the makeup of things drives technological innovation. By manipulating the arrangement and interactions of atoms and molecules, we can unlock new possibilities and address pressing challenges facing humanity.
FAQs about the Makeup of Things
1. What are the different types of chemical bonds?
There are several types of chemical bonds, including:
- Ionic bonds: Involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges that attract each other.
- Covalent bonds: Involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in a stable arrangement where both atoms achieve a full outer shell of electrons.
- Metallic bonds: Involve the sharing of electrons between many atoms, resulting in a "sea of electrons" that holds the metal atoms together.
- Hydrogen bonds: Relatively weak bonds that form between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) and another electronegative atom.
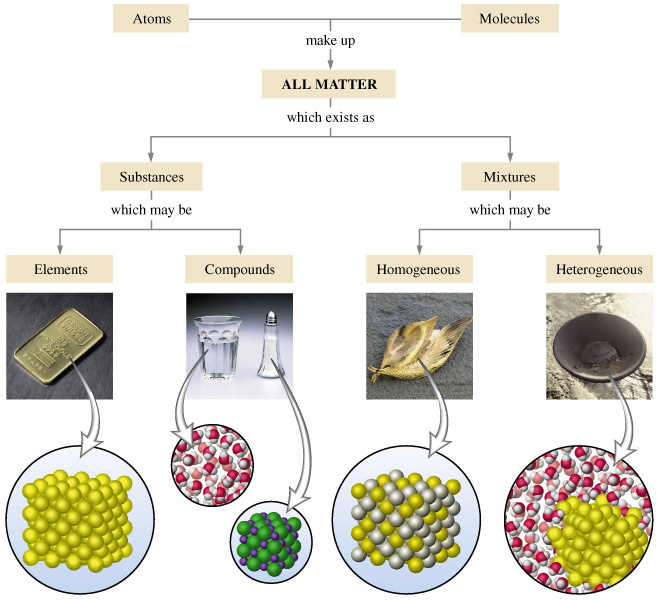
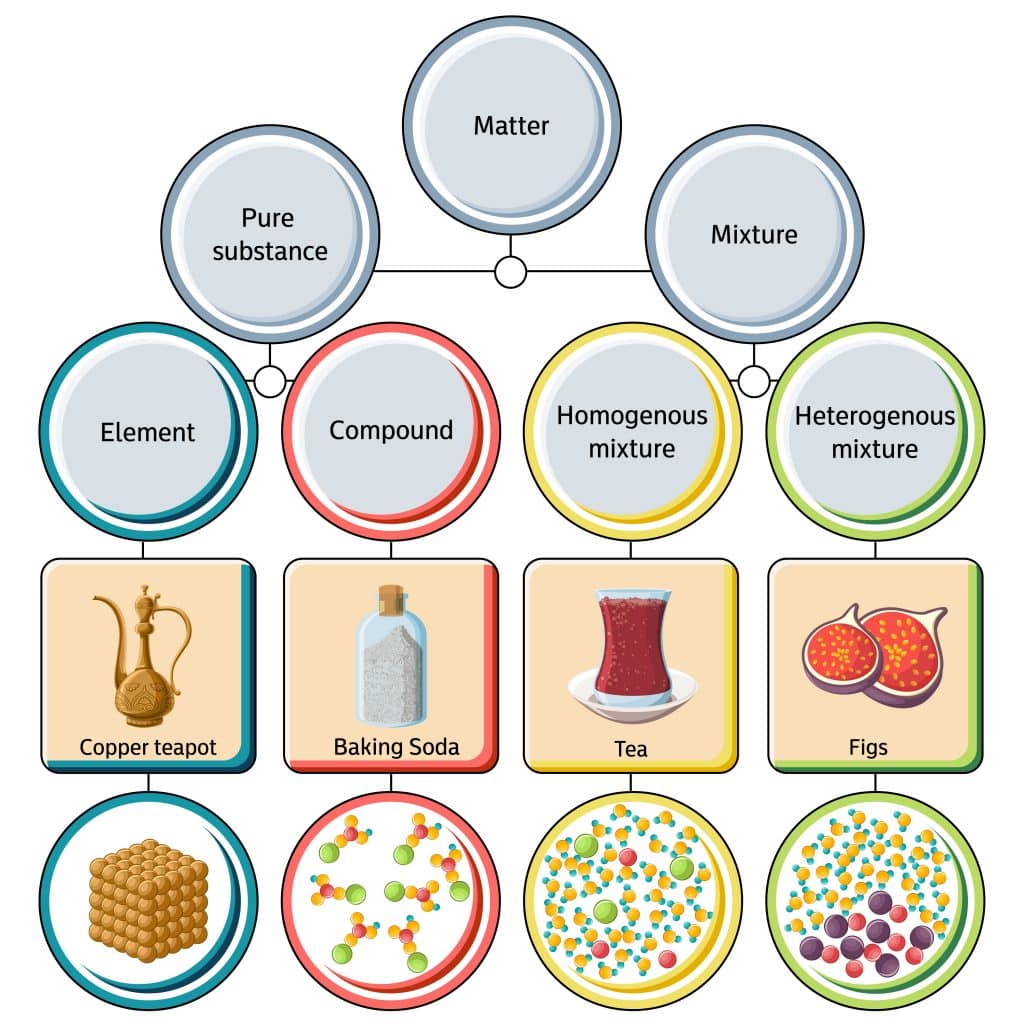
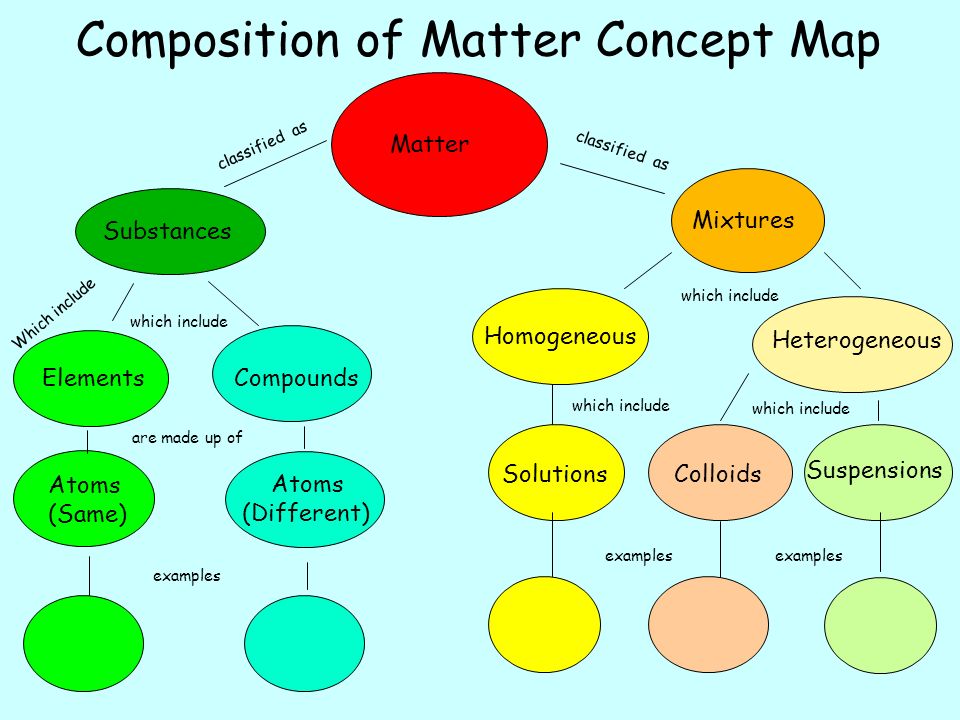
2. What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture?
- Pure substance: A material composed of only one type of atom or molecule. It has a fixed composition and definite properties. Examples include water (H2O), gold (Au), and table salt (NaCl).
- Mixture: A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means. Examples include air (a mixture of gases), seawater (a mixture of water and dissolved salts), and sand (a mixture of different minerals).
3. How can we determine the composition of a substance?
Several techniques can be used to determine the composition of a substance, including:
- Spectroscopy: Techniques that analyze the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter, providing information about the chemical bonds and elements present.
- Chromatography: Techniques that separate the components of a mixture based on their different affinities for a stationary phase and a mobile phase.
- Mass spectrometry: A technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, providing information about the molecular weight and composition of the substance.
Tips for Understanding the Makeup of Things
- Visualize the concepts: Use diagrams, models, and animations to help visualize the arrangement of atoms and molecules.
- Relate to everyday examples: Connect the concepts to familiar materials and objects, such as water, air, and plastics.
- Practice with examples: Work through problems and exercises to solidify your understanding of the concepts.
- Explore further resources: Consult textbooks, websites, and videos for more in-depth information on specific topics.
Conclusion
Understanding the makeup of things is essential for comprehending the world around us. From the fundamental building blocks of atoms to the complex structures of molecules, the composition of matter dictates its properties and behavior. By delving into the fascinating world of elements, compounds, and chemical bonds, we gain insights into the nature of the universe and the diverse materials that shape our lives. This knowledge empowers us to develop new technologies, solve pressing challenges, and appreciate the intricate beauty and complexity of the physical world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Composition of Matter: A Deep Dive into the Makeup of Things. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!