The Earth’s Protective Blanket: A Compositional Breakdown of Our Atmosphere
Related Articles: The Earth’s Protective Blanket: A Compositional Breakdown of Our Atmosphere
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Earth’s Protective Blanket: A Compositional Breakdown of Our Atmosphere. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth’s Protective Blanket: A Compositional Breakdown of Our Atmosphere

The Earth’s atmosphere, a seemingly invisible shield surrounding our planet, plays a crucial role in sustaining life. This gaseous envelope acts as a protective barrier, regulating temperature, filtering harmful radiation, and facilitating weather patterns. Understanding the composition of this vital layer is essential to appreciating its multifaceted functions and the delicate balance it maintains.
A Gaseous Tapestry: The Major Components
The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex mixture of gases, with nitrogen and oxygen dominating the composition. While these gases are the most abundant, their presence in varying proportions is critical for life as we know it.
-
Nitrogen (N2): Comprising approximately 78% of the atmosphere, nitrogen is an inert gas, meaning it does not readily react with other elements. This inertness allows it to act as a stable buffer, preventing rapid fluctuations in atmospheric pressure.
-
Oxygen (O2): Second only to nitrogen, oxygen makes up about 21% of the atmosphere. This vital gas is essential for respiration, powering the metabolic processes of most living organisms. Oxygen also plays a crucial role in the ozone layer, which shields the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
-
Argon (Ar): This inert gas accounts for approximately 0.93% of the atmosphere. Argon is primarily a by-product of radioactive decay and has no known biological function.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): While present in relatively small amounts (approximately 0.04%), carbon dioxide is a potent greenhouse gas. This means it traps heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the Earth’s natural warming effect. While essential for plant photosynthesis, increasing levels of carbon dioxide due to human activities have led to concerns about climate change.
Trace Gases: A Symphony of Influence
Beyond the major constituents, a variety of trace gases exist in the atmosphere, each playing a unique role. These gases, though present in minuscule amounts, can have significant impacts on climate, air quality, and the overall health of the planet.
-
Water Vapor (H2O): This variable component of the atmosphere, ranging from near zero to a few percent, plays a crucial role in weather patterns. Water vapor acts as a powerful greenhouse gas, influencing cloud formation, precipitation, and temperature regulation.
-
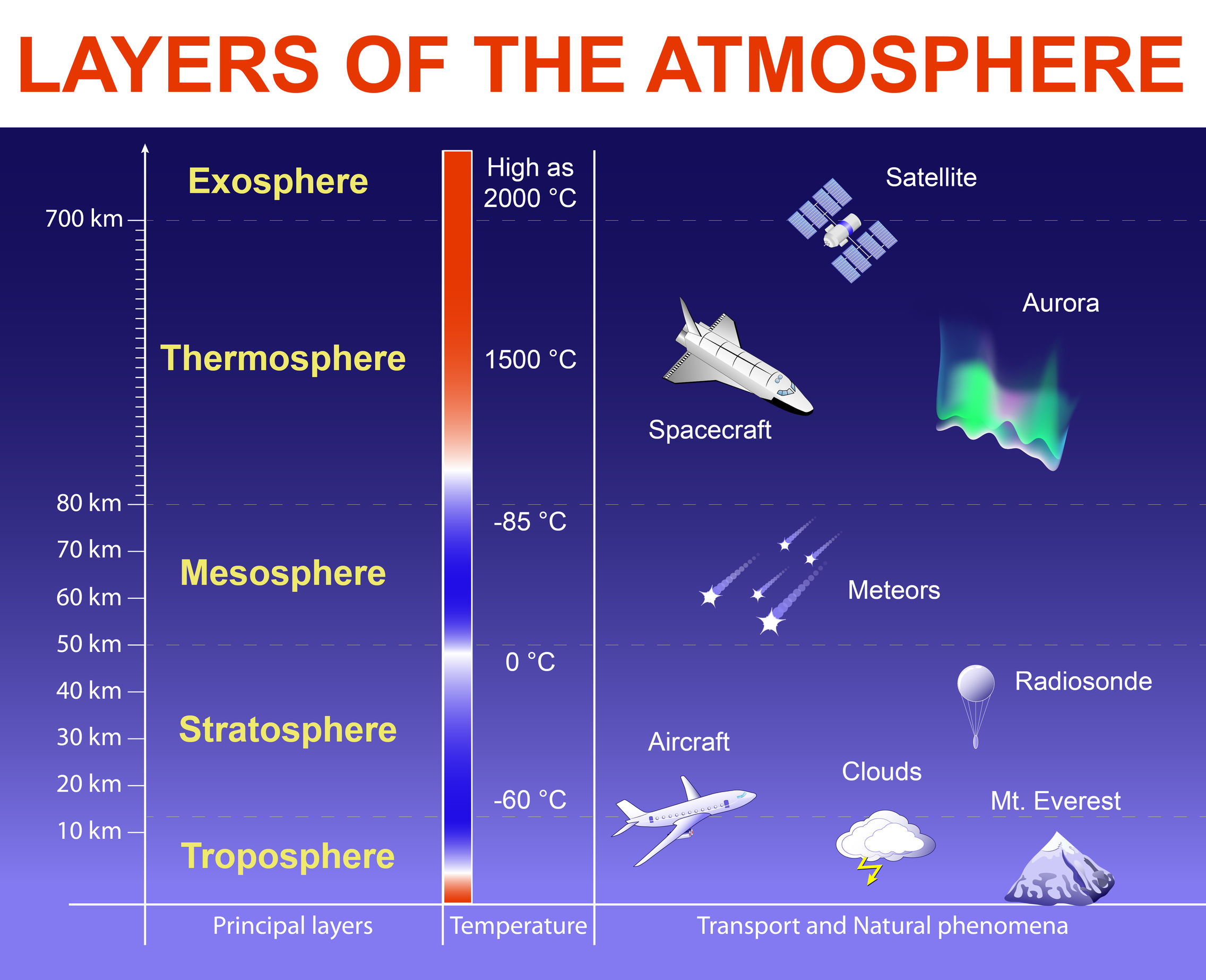
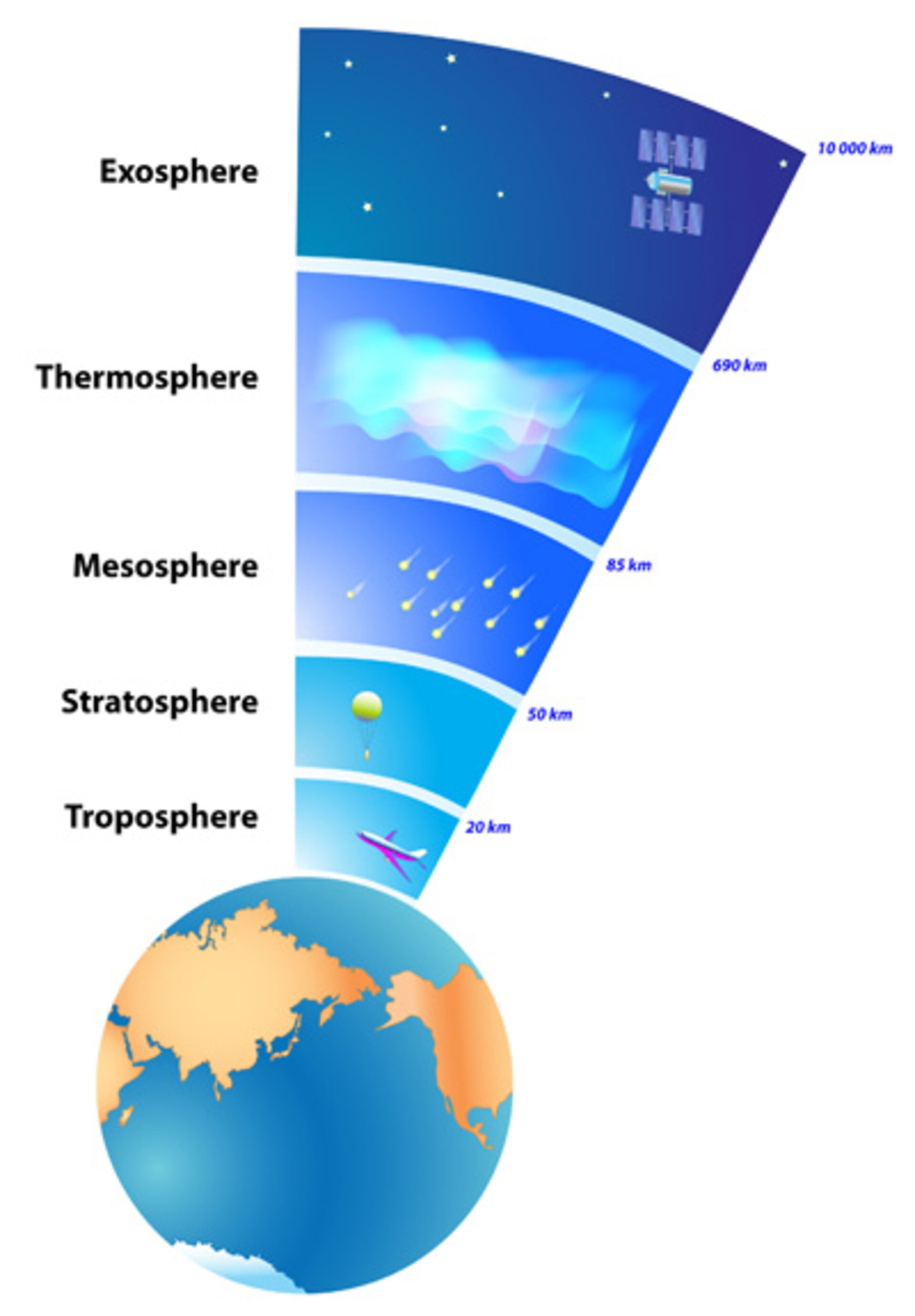
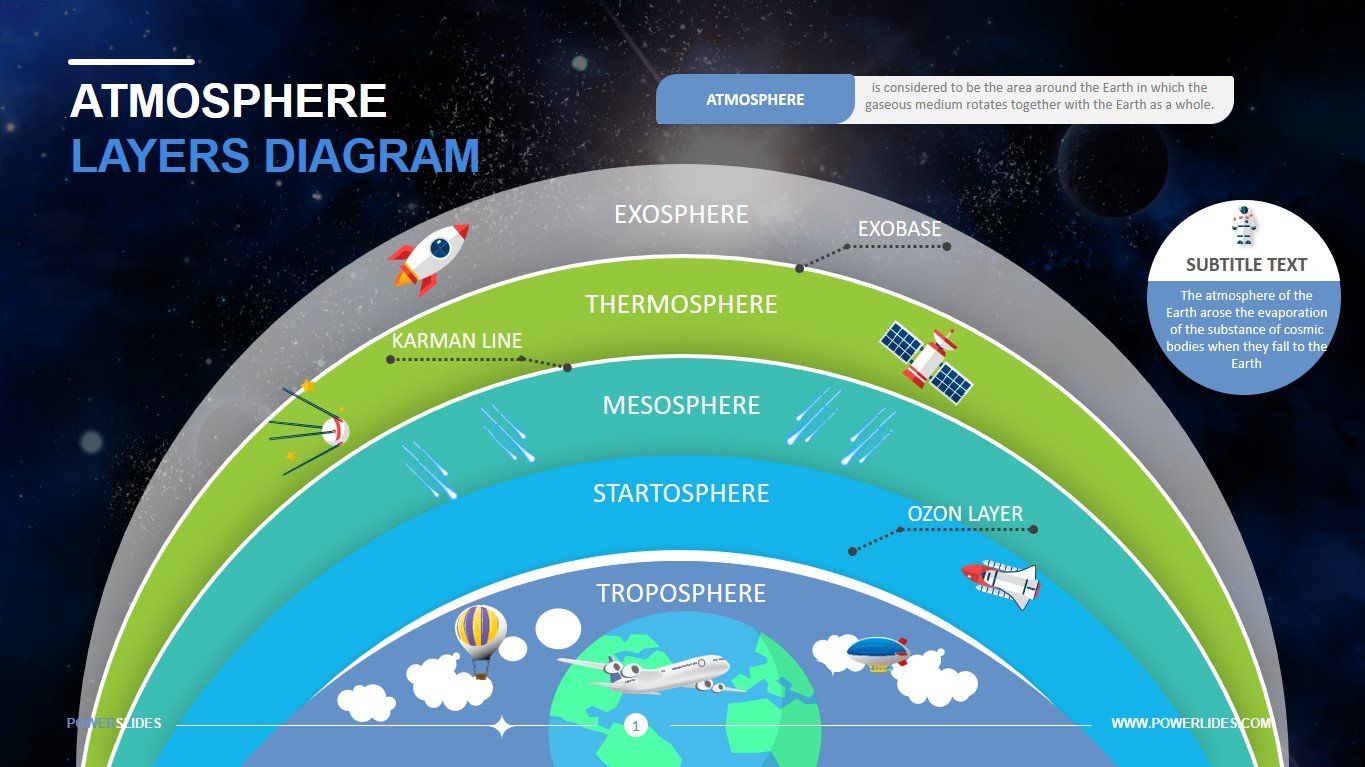
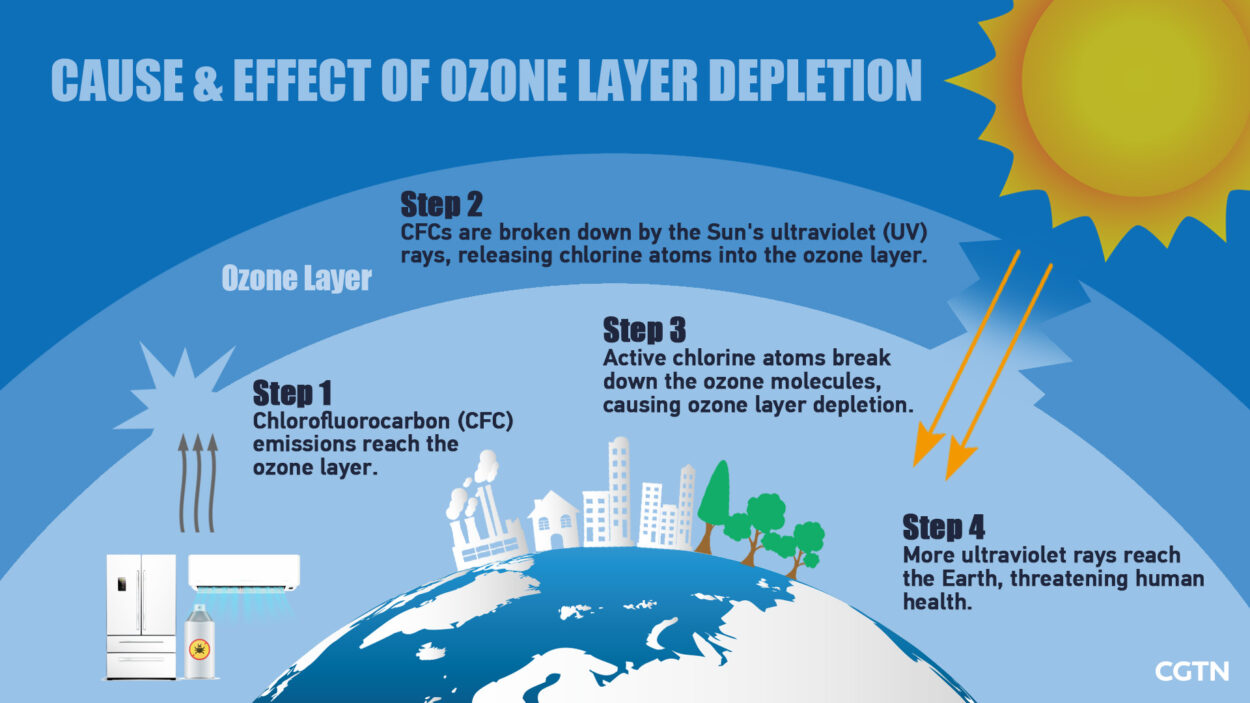
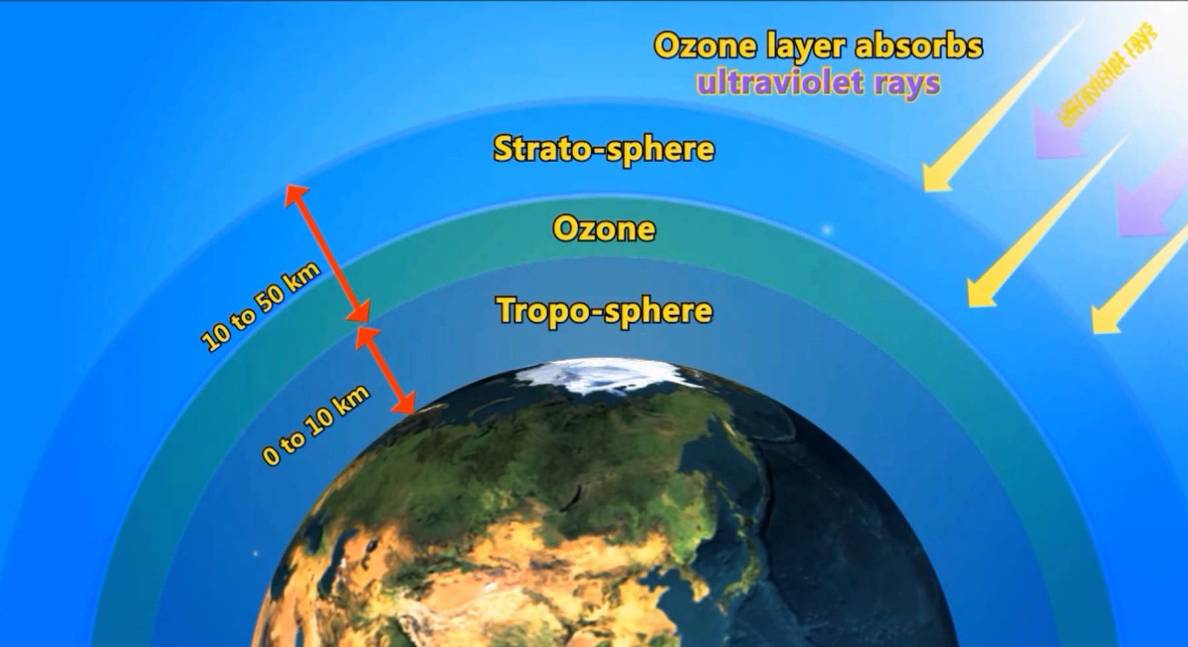
Ozone (O3): Found primarily in the stratosphere, ozone forms a protective layer that absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. While beneficial in the stratosphere, ozone at ground level is a pollutant that can damage human health and the environment.
-
Methane (CH4): A potent greenhouse gas, methane is released from natural sources like wetlands and human activities like fossil fuel extraction. Its presence in the atmosphere contributes to global warming.
-
Nitrous Oxide (N2O): Another potent greenhouse gas, nitrous oxide is released from agricultural activities, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels.
The Dynamic Nature of Atmospheric Composition
The composition of the Earth’s atmosphere is not static. It is constantly changing, influenced by natural processes and human activities. Volcanic eruptions, for instance, can release significant amounts of gases like sulfur dioxide, temporarily altering the atmospheric composition. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have led to a significant increase in greenhouse gas concentrations, with consequences for climate change.
The Importance of Atmospheric Composition
The composition of the Earth’s atmosphere is a delicate balance, crucial for maintaining life and supporting a habitable planet.
-
Climate Regulation: The atmosphere acts as a blanket, regulating temperature by trapping heat from the sun. Greenhouse gases play a vital role in this process, ensuring the Earth remains warm enough to support life.
-
Protection from Harmful Radiation: The ozone layer, a region in the stratosphere rich in ozone, absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the Earth’s surface.
-
Weather and Climate Patterns: The movement of air masses, driven by differences in temperature and pressure, creates weather patterns and contributes to global climate.
-
Air Quality: The composition of the atmosphere directly affects air quality, influencing human health and the environment.
FAQs about the Earth’s Atmosphere
Q: What is the most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere?
A: Nitrogen (N2) comprises approximately 78% of the atmosphere.
Q: How does the Earth’s atmosphere protect us from the sun’s harmful radiation?
A: The ozone layer, found in the stratosphere, absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the Earth’s surface.
Q: What is the role of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere?
A: Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the Earth’s natural warming effect. While essential for maintaining a habitable temperature, increasing levels of greenhouse gases due to human activities have led to concerns about climate change.
Q: How does the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere affect air quality?
A: The presence of pollutants, such as ozone and particulate matter, in the atmosphere can negatively impact air quality, leading to respiratory problems and other health issues.
Q: How does the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere influence weather patterns?
A: The movement of air masses, driven by differences in temperature and pressure, creates weather patterns. Water vapor, a variable component of the atmosphere, plays a crucial role in this process, influencing cloud formation, precipitation, and temperature regulation.
Tips for Understanding the Earth’s Atmosphere
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of scientific research and news related to atmospheric composition and climate change.
-
Reduce Your Carbon Footprint: Take steps to reduce your emissions of greenhouse gases by using public transportation, conserving energy, and supporting sustainable practices.
-
Advocate for Environmental Protection: Support policies and initiatives aimed at protecting the environment and reducing pollution.
-
Educate Others: Share your knowledge about the importance of the Earth’s atmosphere and the impact of human activities on its composition.
Conclusion
The Earth’s atmosphere is a vital component of our planet, essential for sustaining life and maintaining a habitable environment. Understanding the composition of this gaseous envelope, its dynamic nature, and the various roles it plays is crucial for appreciating its importance and the need to protect it. By recognizing the delicate balance of the Earth’s atmosphere and the impact of human activities, we can work towards preserving this vital shield for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth’s Protective Blanket: A Compositional Breakdown of Our Atmosphere. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!