The Earth’s Atmosphere: A Symphony of Gases
Related Articles: The Earth’s Atmosphere: A Symphony of Gases
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Earth’s Atmosphere: A Symphony of Gases. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth’s Atmosphere: A Symphony of Gases

The Earth’s atmosphere, the protective blanket enveloping our planet, is a complex and dynamic system. Its composition, a delicate balance of gases, plays a crucial role in regulating our climate, shielding us from harmful radiation, and supporting life as we know it. This intricate mix of gases, known as the atmospheric composition, is a testament to the delicate equilibrium that governs our planet.
A Closer Look at the Atmospheric Composition
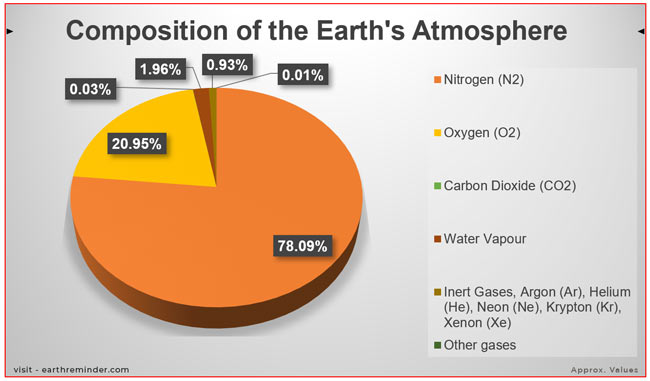
The Earth’s atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), which together constitute about 99% of its volume. While these two gases dominate the atmospheric composition, the remaining 1% comprises a diverse array of trace gases, each playing a vital role in maintaining the Earth’s delicate balance.
Major Components:
- Nitrogen (N2): The most abundant gas in the atmosphere, comprising about 78%, nitrogen is crucial for plant growth and plays a vital role in various biological processes. It is also a key component of the Earth’s protective ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
- Oxygen (O2): The second most abundant gas, oxygen constitutes about 21% of the atmosphere. It is essential for respiration, a fundamental process for all living organisms. Oxygen is also a crucial component of the Earth’s climate system, influencing temperature and weather patterns.
Minor Components:
- Argon (Ar): The third most abundant gas in the atmosphere, argon makes up about 0.93%. It is an inert gas, meaning it does not readily react with other elements. Argon is used in various industrial applications, including welding and lighting.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): While present in relatively small amounts, carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s temperature through the greenhouse effect. It absorbs infrared radiation emitted from the Earth’s surface, trapping heat and contributing to the planet’s warmth.
- Water Vapor (H2O): The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere varies significantly depending on location and season. However, it is a vital component of the Earth’s weather system, contributing to cloud formation, precipitation, and the regulation of temperature.
- Ozone (O3): This gas is found in the stratosphere, forming a protective layer that absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Ozone depletion, caused primarily by human-made chemicals, poses a significant threat to life on Earth.
- Other Trace Gases: The atmosphere also contains trace amounts of other gases, including methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). These gases contribute to the greenhouse effect and can have significant impacts on air quality and climate.
Dynamic Equilibrium: The Importance of Atmospheric Composition
The Earth’s atmospheric composition is not static but constantly in flux. Natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions, photosynthesis, and respiration, contribute to the ongoing cycle of gases in the atmosphere. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly altered the composition of the atmosphere, with far-reaching consequences for our planet.
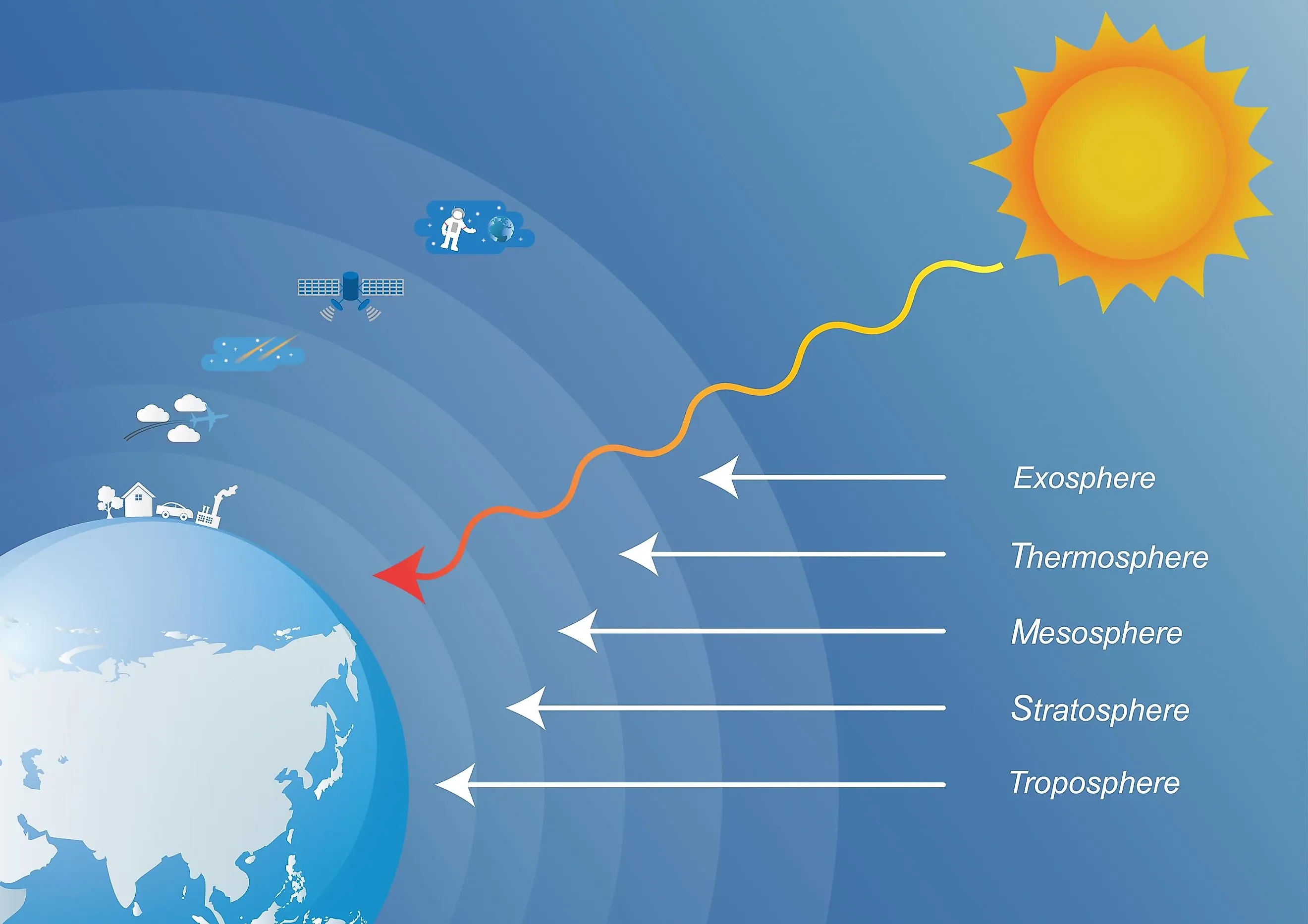
The Greenhouse Effect: A Balancing Act
The greenhouse effect, a natural phenomenon essential for maintaining a habitable Earth, is driven by the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, absorb infrared radiation emitted from the Earth’s surface, trapping heat and warming the planet.
While the greenhouse effect is crucial for sustaining life, excessive levels of greenhouse gases can lead to an imbalance, causing the planet to warm at an accelerated rate. This phenomenon, known as global warming, is a pressing concern, driving changes in weather patterns, rising sea levels, and a multitude of other environmental challenges.
The Ozone Layer: A Protective Shield
The ozone layer, a region in the stratosphere containing high concentrations of ozone, acts as a protective shield, absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. This radiation can cause skin cancer, cataracts, and other health problems.
However, the ozone layer is under threat from human activities, particularly the release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances. The depletion of the ozone layer has significant consequences for human health and the environment, highlighting the importance of protecting this vital atmospheric component.
The Role of Atmospheric Composition in Climate Change
The composition of the Earth’s atmosphere is inextricably linked to climate change. The increasing concentration of greenhouse gases, primarily due to human activities, is driving global warming and its associated consequences. Understanding the role of atmospheric composition in climate change is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its impacts.
FAQs about Atmospheric Composition
1. What are the major components of the Earth’s atmosphere?
The major components of the Earth’s atmosphere are nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), which together constitute about 99% of its volume.
2. What is the greenhouse effect, and how does it impact climate change?
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon where greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun, warming the planet. However, excessive levels of greenhouse gases can lead to an imbalance, causing global warming.
3. What is the ozone layer, and why is it important?
The ozone layer is a region in the stratosphere containing high concentrations of ozone, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Ozone depletion poses a significant threat to life on Earth.
4. How do human activities impact atmospheric composition?
Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, release greenhouse gases and other pollutants into the atmosphere, altering its composition and contributing to climate change.
5. What are the consequences of climate change?
Climate change has a multitude of consequences, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, changes in agricultural yields, and impacts on biodiversity.
Tips for Understanding Atmospheric Composition
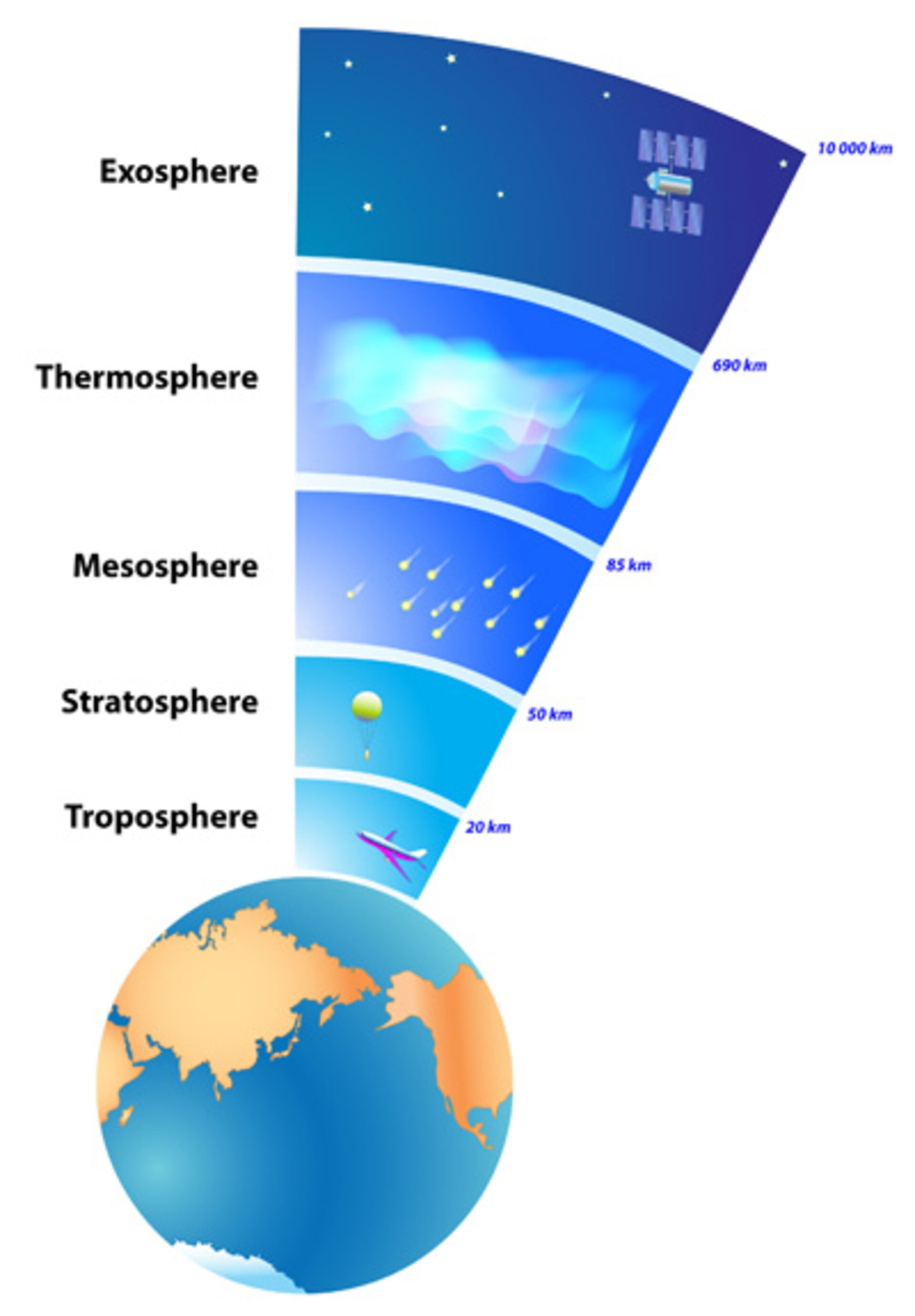
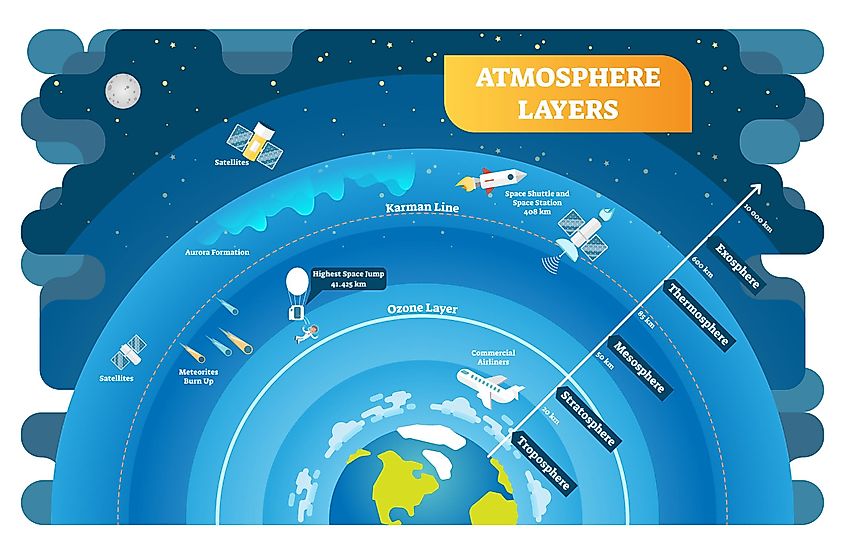
- Visualize the atmosphere: Imagine the atmosphere as a layered blanket surrounding the Earth, with different gases distributed throughout its layers.
- Explore the role of each gas: Learn about the specific functions of each gas in the atmosphere, such as nitrogen’s role in plant growth and oxygen’s role in respiration.
- Connect atmospheric composition to climate change: Understand how the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases contributes to global warming and its consequences.
- Engage with climate science: Stay informed about ongoing research and initiatives related to atmospheric composition and climate change.
Conclusion
The Earth’s atmosphere, a delicate balance of gases, is crucial for regulating our climate, shielding us from harmful radiation, and supporting life as we know it. Understanding the composition of the atmosphere and its dynamic equilibrium is essential for addressing the challenges posed by climate change and protecting our planet for future generations. By embracing a deeper understanding of this intricate system, we can work towards ensuring a sustainable future for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth’s Atmosphere: A Symphony of Gases. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!