The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Pillar of American Democracy
Related Articles: The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Pillar of American Democracy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Pillar of American Democracy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Pillar of American Democracy

The United States Senate, one of the two legislative bodies of the federal government, stands as a crucial element in the nation’s democratic framework. Its unique structure, with equal representation for each state regardless of population, ensures a balance of power between large and small states, fostering a sense of unity and shared governance. Understanding the makeup of the Senate, its historical evolution, and its role in shaping legislation is essential for comprehending the intricacies of American politics.
The Senate’s Composition: A Two-Tiered System
The Senate comprises 100 members, two from each of the 50 states. This equal representation, enshrined in the Constitution, stands in contrast to the House of Representatives, where representation is based on population. This fundamental difference reflects the founding fathers’ desire to safeguard the interests of smaller states, preventing dominance by more populous ones.
A Bipartisan Landscape: Democrats and Republicans
The Senate’s political landscape is characterized by a two-party system, with the majority of senators aligning themselves with either the Democratic or Republican parties. While there have been instances of independent senators or members of other parties, the two-party system has dominated the Senate’s dynamics for decades.
The Role of the Senate in Legislation
The Senate plays a pivotal role in the legislative process, sharing power with the House of Representatives in enacting laws. Bills must pass both chambers before being sent to the President for signature. The Senate’s unique structure and its deliberative nature, with its power to filibuster and require a supermajority vote for certain legislation, allow for thorough debate and consideration of proposed laws.
Historical Evolution of the Senate’s Makeup
The composition of the Senate has evolved over time, reflecting societal changes and political shifts. Initially, senators were chosen by state legislatures, a system that was later replaced by direct election through the 17th Amendment in 1913. This change democratized the process, giving voters a more direct say in who represents them in the Senate.
The Senate’s Importance: A Balancing Act
The Senate’s composition, with its equal representation for each state and its deliberative processes, ensures that a wide range of perspectives are considered in lawmaking. This system, while not without its critics, has fostered a balance between the interests of large and small states, promoting a sense of national unity and shared governance.
Benefits of the Senate’s Makeup
The Senate’s structure offers several benefits:
- Equal Representation: It guarantees that all states, regardless of size, have an equal voice in the legislative process.
- Deliberative Process: The Senate’s rules and procedures, including the filibuster, encourage thoughtful debate and thorough consideration of legislation.
- Checks and Balances: The Senate acts as a check on the power of the House of Representatives and the President, ensuring a system of checks and balances in the government.
- Stability: The Senate’s relatively small size and long terms (six years) contribute to a more stable and less volatile political landscape compared to the House of Representatives.
FAQs on the Makeup of the Senate
Q: How are senators elected?
A: Senators are elected by the people of their respective states through direct elections.
Q: How long are Senate terms?
A: Senators serve six-year terms, with staggered elections ensuring that only one-third of the Senate is up for election every two years.
Q: What are the qualifications to be a senator?
A: To be a senator, one must be at least 30 years old, a U.S. citizen for at least nine years, and a resident of the state they represent.
Q: What is the role of the Senate Majority Leader?
A: The Senate Majority Leader, elected by the majority party, is responsible for setting the legislative agenda, scheduling debates, and coordinating the party’s strategy in the Senate.
Q: What is the role of the Senate Minority Leader?
A: The Senate Minority Leader, elected by the minority party, leads the opposition and works to advance the minority party’s agenda.
Tips for Understanding the Senate’s Makeup
- Follow Senate proceedings: Stay informed about the activities of the Senate by reading news articles, watching congressional hearings, and following senators on social media.
- Engage with your senators: Contact your senators to express your views on important issues and to learn about their positions on legislation.
- Learn about the Senate’s history: Understanding the historical evolution of the Senate can provide valuable context for current events.
- Explore resources: Numerous websites and organizations offer information about the Senate, including the Senate’s official website, the Congressional Budget Office, and the Congressional Research Service.
Conclusion
The makeup of the United States Senate, with its equal representation, deliberative processes, and two-party system, is a complex yet essential element of American democracy. Its structure and functions contribute to the stability of the government, ensuring that a wide range of perspectives are considered in the legislative process. Understanding the Senate’s composition and its role in shaping legislation is crucial for informed civic engagement and a deeper understanding of the American political system.


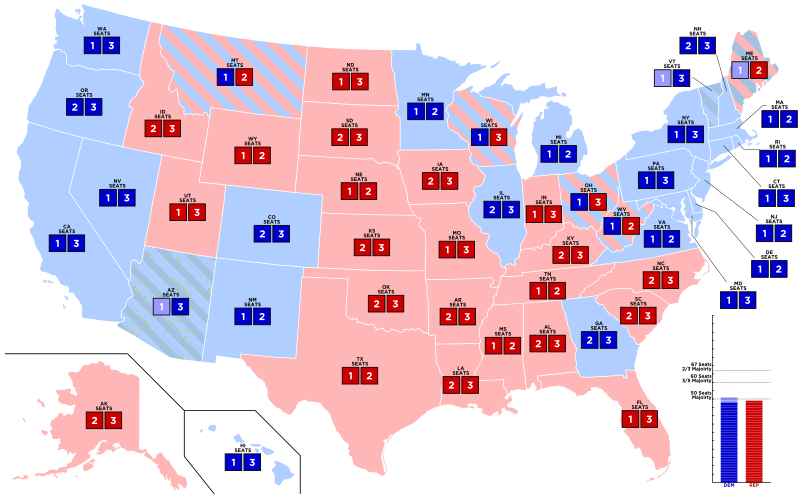

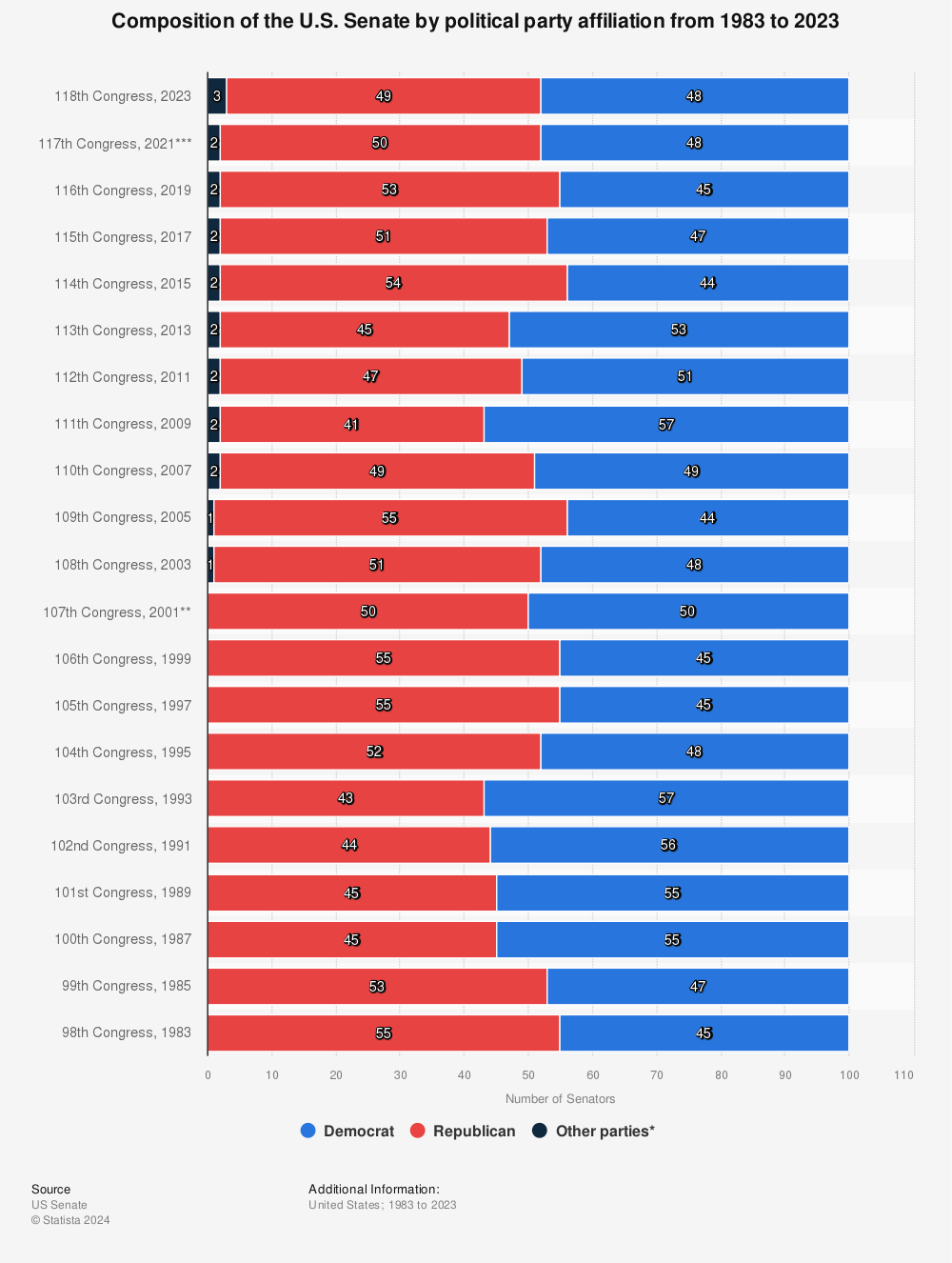

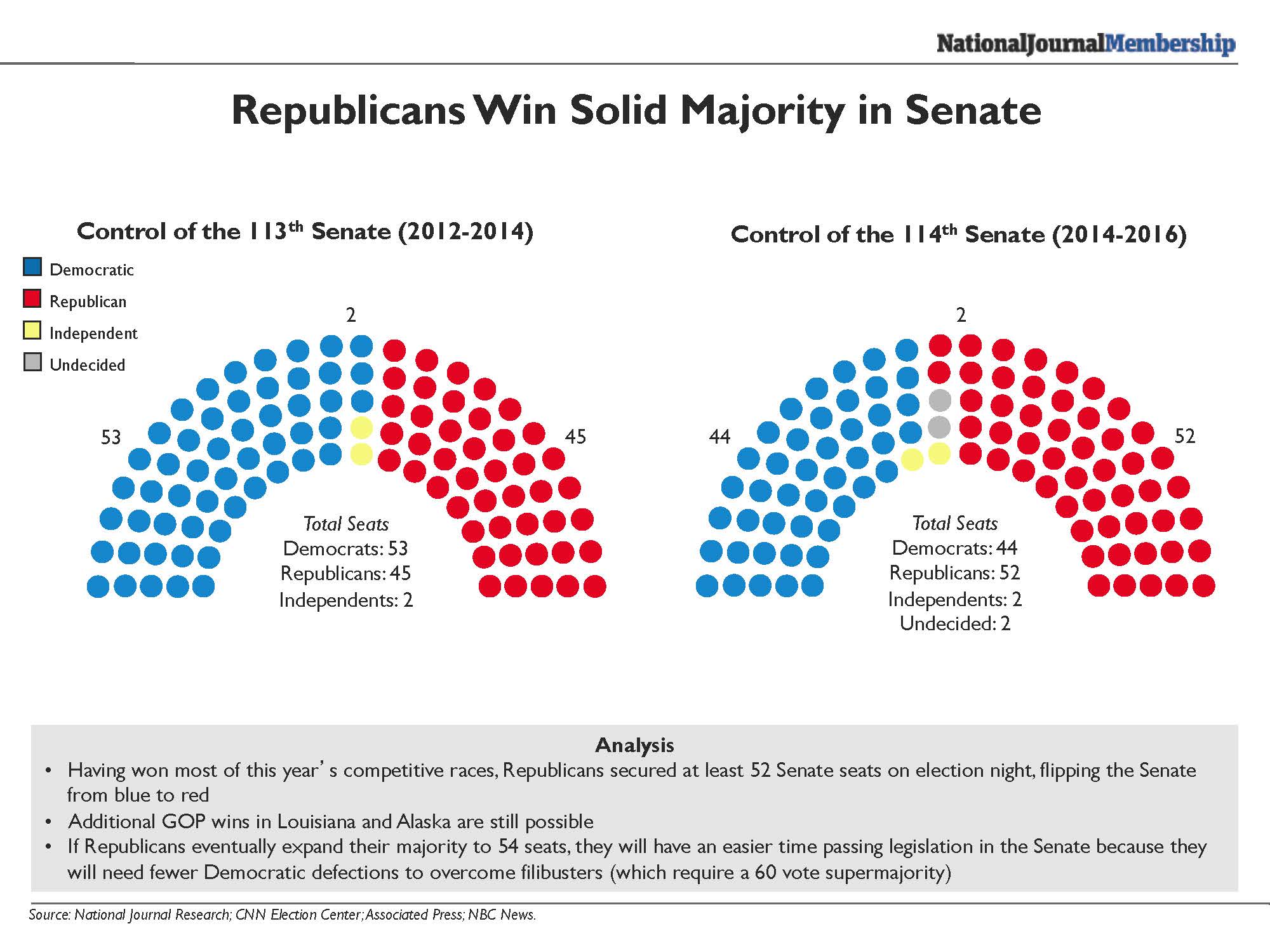

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Pillar of American Democracy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!