The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life
Related Articles: The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life
- 3.1 The Major Players: Nitrogen and Oxygen
- 3.2 Trace Gases: Essential in Small Doses
- 3.3 Water Vapor: The Variable Factor
- 3.4 The Importance of Atmospheric Composition
- 3.5 The Impact of Human Activities
- 3.6 The Importance of Monitoring Atmospheric Composition
- 3.7 Frequently Asked Questions about the Composition of Air
- 3.8 Tips for Understanding and Protecting the Air We Breathe
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life
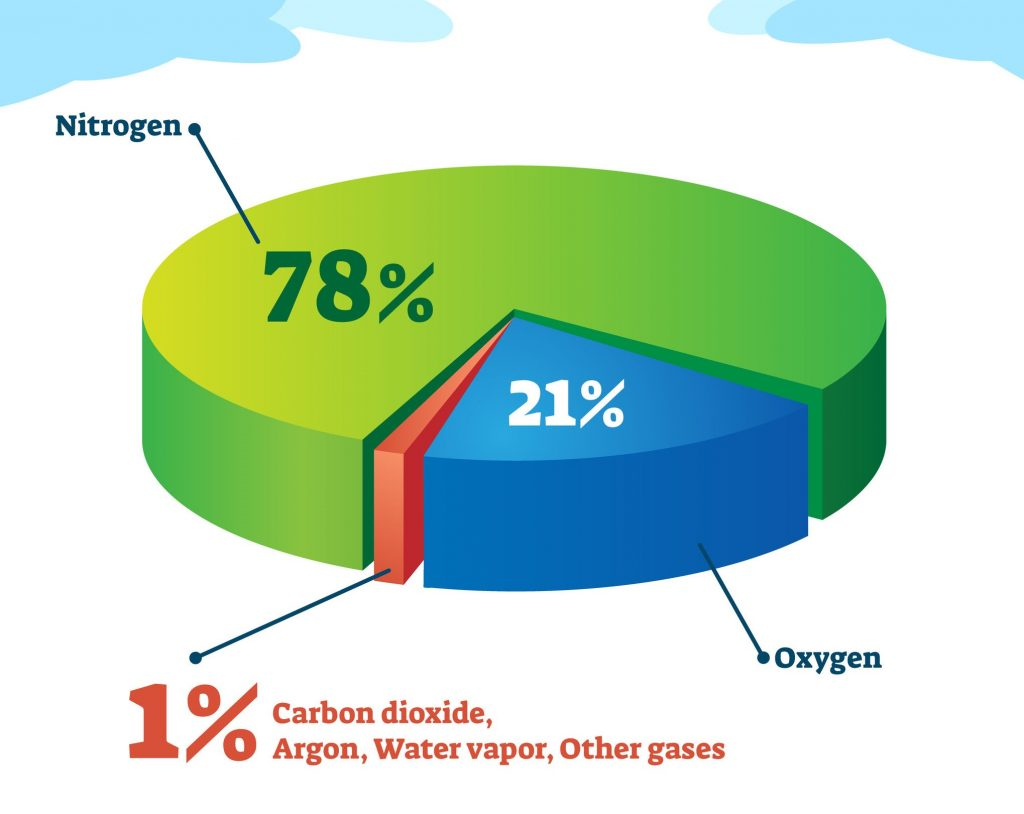
The air we breathe, the very essence of our existence, is a complex mixture of gases. This invisible blanket surrounding our planet is not a single entity, but rather a carefully balanced cocktail of elements that are crucial for sustaining life. Understanding the composition of this air is essential for comprehending the delicate balance of our environment and the impact of human activities on it.
The Major Players: Nitrogen and Oxygen
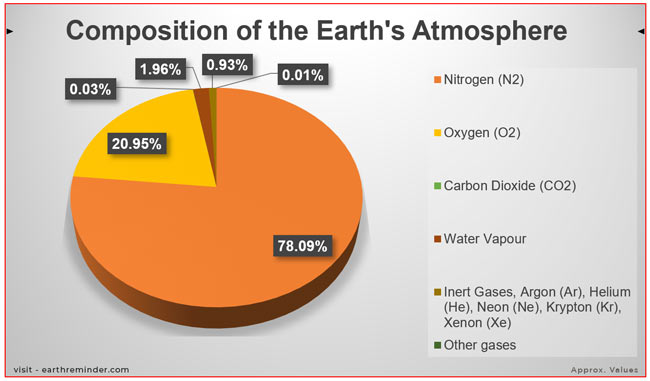
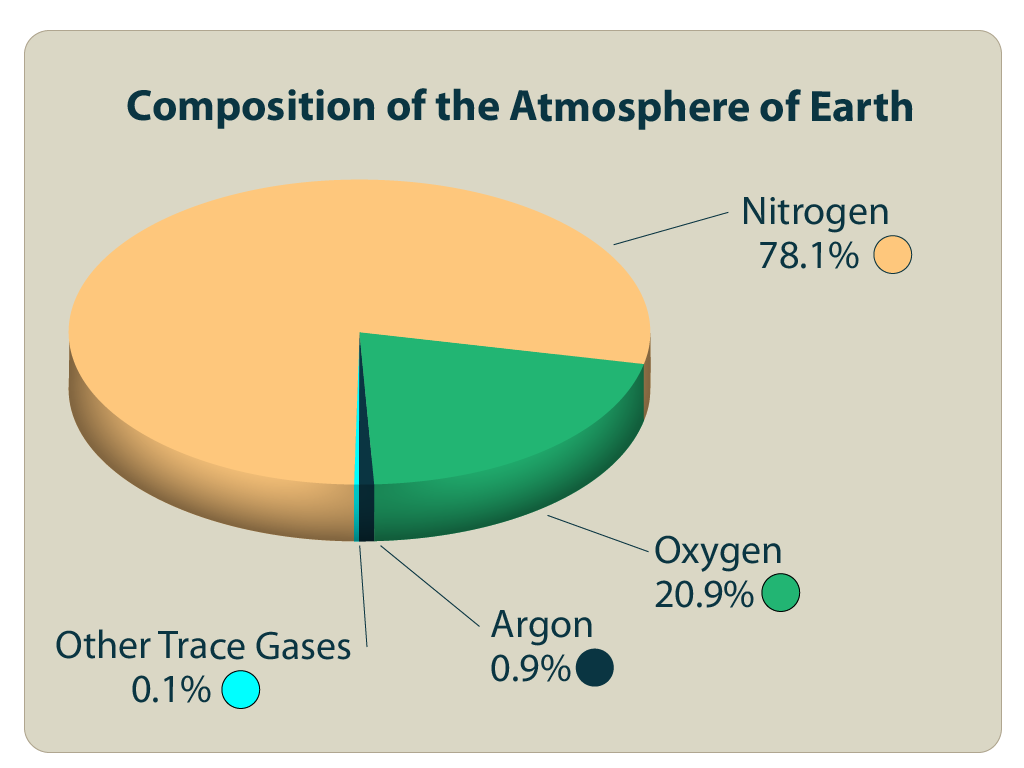
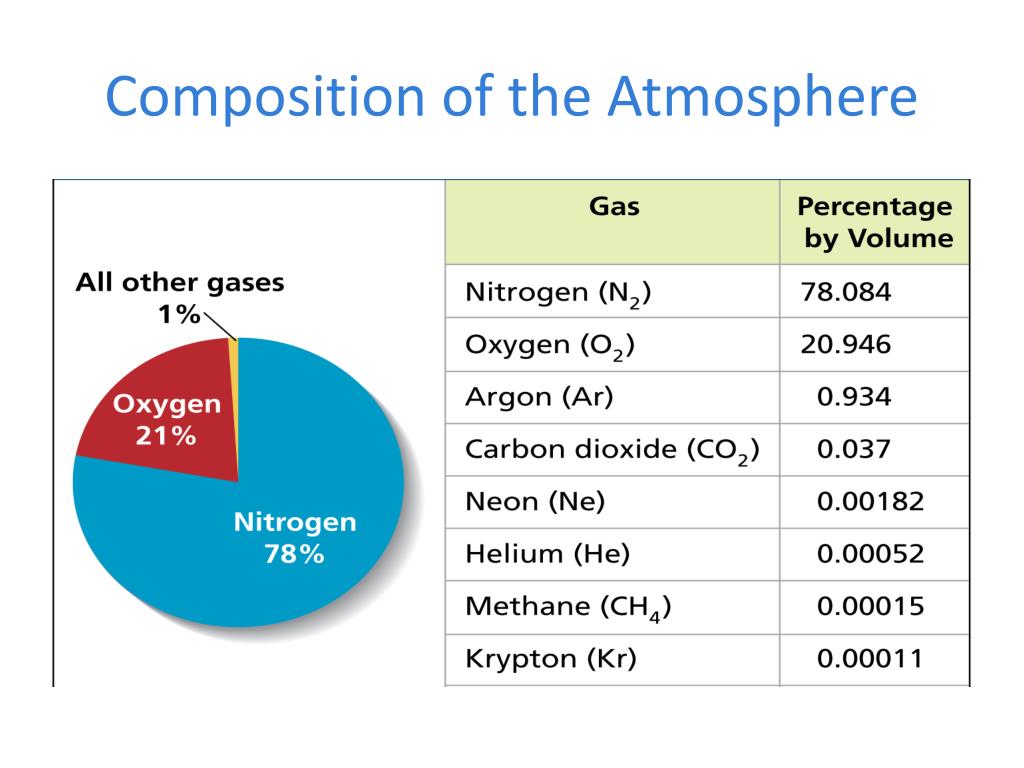
The two most abundant components of Earth’s atmosphere are nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2). Nitrogen, comprising approximately 78% of the air, is a relatively inert gas, meaning it does not readily react with other substances. While crucial for plant growth, its primary role in the atmosphere is as a diluting agent, preventing the concentration of oxygen from becoming too high.
Oxygen, at around 21%, is the lifeblood of our planet. It is essential for respiration, the process by which living organisms convert food into energy. Oxygen is also vital for combustion, the process that fuels our industries and powers our lives.
Trace Gases: Essential in Small Doses
While nitrogen and oxygen dominate the atmospheric composition, a diverse array of trace gases plays crucial roles in maintaining Earth’s delicate climate balance and supporting life. These include:
- Argon (Ar): This inert gas comprises approximately 0.93% of the atmosphere and is primarily a product of radioactive decay. It is used in various industrial applications, including welding and lighting.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Though present in a relatively small amount (around 0.04%), carbon dioxide is a potent greenhouse gas. It absorbs heat radiated from the Earth’s surface, contributing to the planet’s temperature regulation. However, the increasing concentration of CO2 due to human activities is a primary driver of climate change.
- Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH4), Krypton (Kr), Hydrogen (H2), and Xenon (Xe): These gases are present in even smaller quantities, but they have significant roles in various atmospheric processes, including ozone formation and atmospheric chemistry.
Water Vapor: The Variable Factor
Water vapor, the gaseous form of water, is a highly variable component of the atmosphere, ranging from near zero in dry desert regions to over 4% in humid tropical areas. Water vapor is a potent greenhouse gas, absorbing heat and contributing to the Earth’s temperature regulation. It also plays a crucial role in the formation of clouds and precipitation.
The Importance of Atmospheric Composition
The precise composition of Earth’s atmosphere is not a random occurrence. This carefully balanced mixture of gases has evolved over billions of years, creating the conditions necessary for life to flourish. The relative abundance of oxygen supports respiration and combustion, while the presence of carbon dioxide and water vapor regulates the planet’s temperature. The inert gases, like nitrogen and argon, provide stability and dilution, preventing extreme fluctuations in the atmospheric composition.
The Impact of Human Activities
Human activities are altering the composition of Earth’s atmosphere at an unprecedented rate. The burning of fossil fuels releases vast amounts of carbon dioxide, increasing its concentration in the atmosphere and contributing to climate change. Other pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, are released into the atmosphere, contributing to acid rain and smog.
The Importance of Monitoring Atmospheric Composition
Monitoring the composition of Earth’s atmosphere is crucial for understanding the impact of human activities on the environment and for developing strategies to mitigate these impacts. Scientists use various methods to track changes in atmospheric composition, including ground-based monitoring stations, satellites, and aircraft.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Composition of Air
1. What is the main component of air?
The most abundant component of air is nitrogen, making up approximately 78% of the atmosphere.
2. How does the composition of air affect the Earth’s climate?
The composition of air, particularly the presence of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, plays a significant role in regulating the Earth’s temperature.
3. How does human activity affect the composition of air?
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, release pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, altering its composition.
4. What is the importance of monitoring the composition of air?
Monitoring the composition of air helps us understand the impact of human activities on the environment and develop strategies to mitigate these impacts.
5. What are some of the consequences of changes in the composition of air?
Changes in the composition of air can lead to various consequences, including climate change, air pollution, and acid rain.
Tips for Understanding and Protecting the Air We Breathe
- Reduce your carbon footprint: Make conscious choices to reduce your reliance on fossil fuels by using public transportation, cycling, or walking.
- Support sustainable practices: Choose products and services that are environmentally friendly and support businesses committed to sustainability.
- Educate yourself and others: Learn about the importance of air quality and share your knowledge with friends and family.
- Advocate for policies that protect the environment: Support policies that promote clean energy and reduce pollution.
Conclusion
The composition of Earth’s atmosphere is a testament to the delicate balance of nature. This carefully crafted blend of gases supports life, regulates the planet’s temperature, and provides the foundation for a healthy environment. However, human activities are disrupting this balance, with potentially dire consequences. Understanding the composition of air and its importance is crucial for appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet and for taking action to protect the air we breathe.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere: A Vital Blend for Life. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!